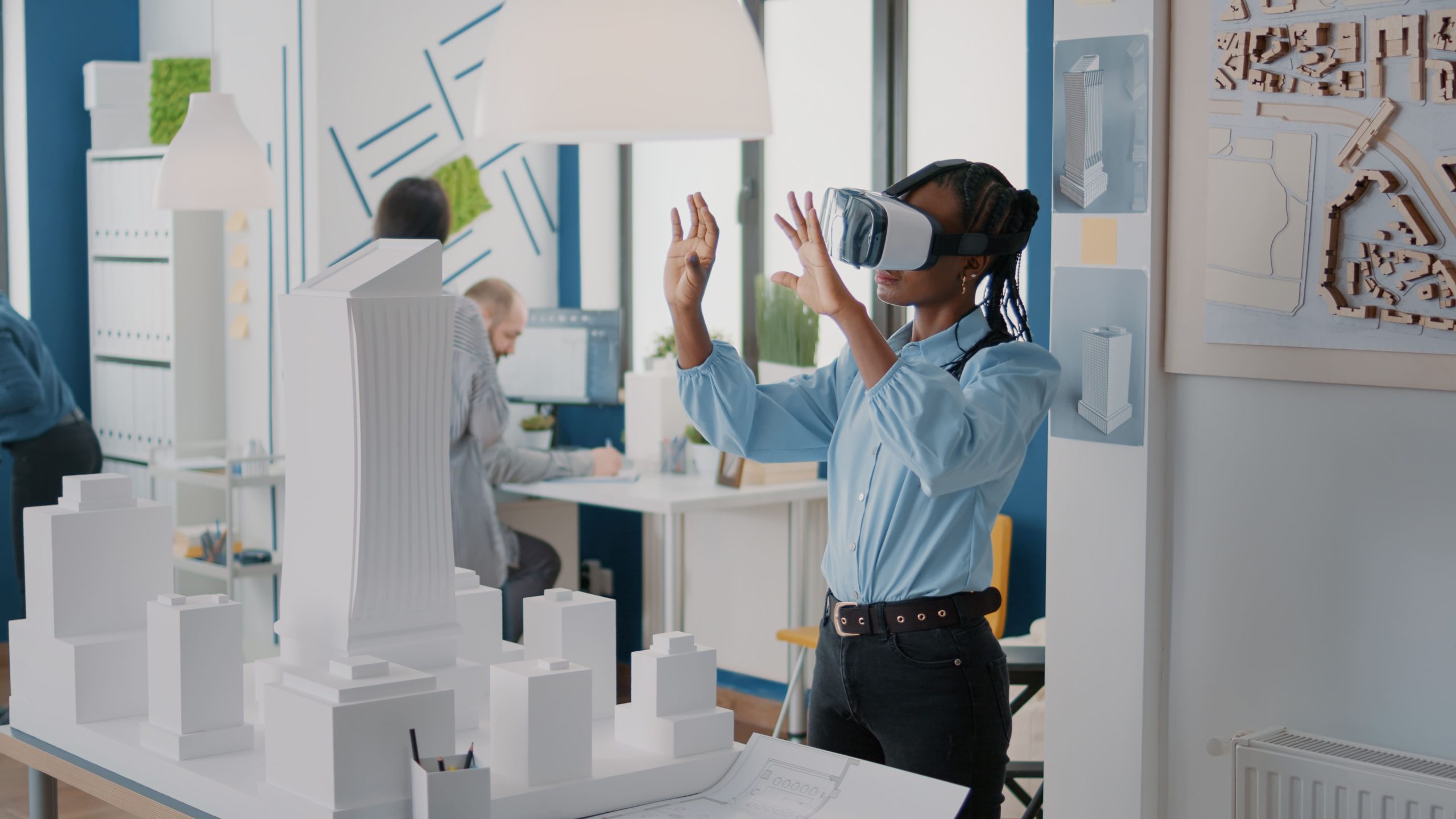
Augmented Reality (AR) is a captivating and transformative technology that enriches the real world by overlaying digital information and virtual objects onto it. In this comprehensive exploration, we will dive into the intriguing realm of Augmented Reality, uncovering its fundamental principles, understanding its unique capabilities, exploring its applications across diverse industries, and recognizing its potential to revolutionize our interaction with the physical environment.
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is a dynamic and immersive technology that enhances our perception of the physical world by seamlessly integrating digital elements into it. It achieves this by superimposing digital information, such as text, images, videos, 3D models, or animations, onto the user’s view of the real world. AR experiences are typically accessed through devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and heads-up displays.
Key characteristics of Augmented Reality (AR):
- Real-World Overlay: AR enhances the real-world environment by overlaying digital content onto it. Users can see both the real world and digital information simultaneously.
- Interactivity: AR encourages user interaction with digital overlays. Users can manipulate, engage with, and receive real-time information from AR elements.
- Contextual Information: AR provides contextually relevant information based on the user’s location, surroundings, and interests. This information is often displayed in real-time.
- Enhanced Perception: AR enhances the user’s perception by providing additional details, explanations, or visualizations of objects and scenes in the real world.
Significance of Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) holds immense significance across various domains, shaping the way we interact with information, objects, and the environment:
- Enhanced user experiences: AR enriches consumer experiences by introducing interactive and immersive elements. This is particularly evident in areas like gaming, retail, and live events.
- Education and training: AR is revolutionizing education and training by offering immersive experiences. Students can explore complex subjects and historical events in lifelike environments, while professionals benefit from hands-on training in various industries.
- Remote support: AR facilitates remote support by allowing experts to guide and provide visual instructions to users in real-time. This is invaluable in fields like maintenance and repair.
- Navigation: AR-based navigation apps provide real-time directions and information about points of interest, simplifying travel and exploration.
- Medical visualization: AR is utilized in medicine to visualize complex anatomical structures and aid in surgical procedures. Surgeons can access detailed information during operations.
Applications of Augmented Reality (AR)
The versatility of Augmented Reality (AR) technology translates into a multitude of applications across diverse industries:
1. Gaming and entertainment: AR has transformed gaming and entertainment by bringing digital characters and objects into the real world. Users can engage in augmented reality games and experiences that blend the virtual with the physical.
2. Education and training: AR is redefining education and training through interactive simulations, virtual laboratories, and immersive learning experiences. Students can explore scientific concepts and historical events with unprecedented depth.
3. Retail and marketing: AR enhances the shopping experience by allowing customers to visualize products in their real-world surroundings before making a purchase decision. It also serves as a powerful tool for immersive advertising and marketing campaigns.
4. Remote assistance: AR enables remote experts to provide guidance and support to users in different locations. This is particularly valuable for technical support, field service, and complex tasks.
5. Healthcare: AR plays a pivotal role in medical training, surgery planning, and patient education. Surgeons can visualize and plan procedures using AR, and patients can gain a better understanding of their conditions through interactive AR visuals.
6. Industrial applications: AR assists workers in various industries, such as manufacturing and maintenance, by providing real-time information and guidance directly in their field of view. This improves efficiency and reduces errors.
Implementing Augmented Reality (AR)
The successful implementation of Augmented Reality (AR) experiences involves several key steps and considerations:
- Hardware: AR experiences require compatible hardware devices, such as smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, or heads-up displays, depending on the target audience and purpose.
- Content creation: AR experiences rely on the creation of digital content, including 3D models, interactive applications, simulations, and augmented narratives.
- Development platforms: Developers use AR development platforms and tools to design, build, test, and deploy AR applications for various platforms and devices.
- Integration: AR solutions may require integration with existing systems, software, and infrastructure to ensure seamless functionality and data synchronization.
- User training: End users may require training on how to use AR applications effectively, ensuring a smooth and productive user experience.
- Content distribution: AR content can be distributed through app stores, online platforms, or enterprise networks, depending on the target audience and deployment strategy.
The future of Augmented Reality (AR)
The future of Augmented Reality (AR) is filled with promise as the technology continues to evolve and find new applications. Key considerations for the future include:
- Advancements in wearables: The development of AR glasses and other wearable devices will enhance the convenience and ubiquity of AR experiences, making them more integrated into our daily lives.
- Improved content creation: Advancements in AR content creation tools and techniques will empower creators to develop more compelling and realistic AR experiences.
- Enhanced interactivity: Future AR experiences may offer even greater interactivity and immersion, blurring the lines between the digital and physical worlds.
- Industry-specific solutions: Tailored AR solutions will continue to emerge, addressing the unique needs of various industries, from healthcare and education to entertainment and manufacturing.
Augmented Reality (AR) represents a remarkable fusion of the digital and physical worlds, offering immersive experiences that span entertainment, education, industry, and beyond. As AR technologies continue to advance, they are poised to play an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of digital interactions and experiences. With limitless possibilities on the horizon, AR stands as a transformative force in the ongoing evolution of our digital landscape.